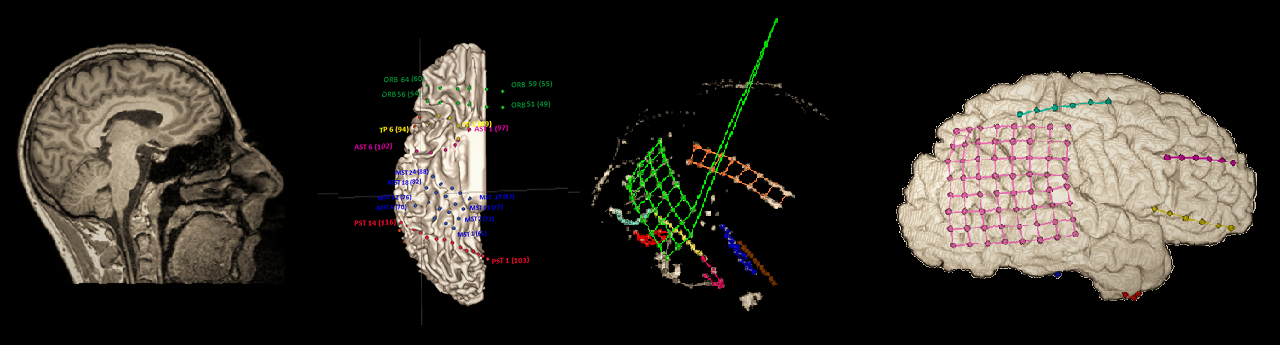
Intracranial EEG (ECoG) anatomical processing and electrode reconstruction pipeline
The scripts and functions available here serve to perform anatomical processing and electrode reconstruction of intracranial data. The code is structured as one central script (ECoG_Electrode_Reconstruction_Script.m) that is executed one code cell at a time, calling additional functions and opening external software packages such as BioImage Suite or MRIcron. That is, the entire process is encapsulated by this script even though some parts of it are performed outside of Matlab. Note that some modifications may be required for depth electrodes as the pipeline was written with surface electrodes in mind, though these should be minimal if any.
The code
The scripts and functions are available on GitHub. To use the code, simply open ECoG_Electrode_Reconstruction_Script.m, make any needed modifications and run the script on a cell-by-cell basis.
Input
The pipeline assumes the following input data:
- Structural MRI scan
- post-surgery CT scan (to identify electrodes)
Processing steps
The pipeline performs the following operations:
- Run FreeSurfer on the MRI scan to generate a registered and parcellated cortical surface.
- Run SUMA (by AFNI) to create a standardized mesh based on the FreeSurfer surfaces. The SUMA mesh is very convenient to work with as it transforms the individual brain surface into a standardized mesh, such that the shape of the brain is maintained but the number and identify of mesh nodes is consistent across individuals (so that node #3534 is located e.g. on the temporal pole in every brain, allowing very comparisons between individuals).
- Generate normalized, skull-stripped and cortex-only nifti images from the FreeSurfer output.
- Register the CT to the MRI image, to map CT-based electorde coordinates to the MRI space (this doesn’t always work smoothly, so there are several optional paths to making it work).
- Manually identify electrode locations, using BioImage Suite. I found that BioImage Suite is the most convenient software to perform this somewhat painstaking labor. Its downside is that it is a standalone software, not readily integrated with other aspects of the analysis - however this is handled in this pipline with dedicated Matlab functions that perform the necessary import and export operations.
- Import the FreeSurfer-generated cortical surface data into Matlab, generating a Matlab structure that holds the anatomical mesh information and can be plotted as a 3D image.
- Reduce errors in electrode coordinates by projecting them to the cortical surface. Inaccuracies are usually encountered due to the differences between the MRI and CT scans, especially if they were taken before and after the operation. This step applies a simple gradient-descent algorithm that finds the nearest place on the cortical surface for the electrode grids without distorting their shape.
- Map electrode coordiantes to the standardized SUMA pial and inflated surfaces.
- Import cortical surface metadata: thickness, curvature, and anatomical parcellation data.
- Visualize the electrodes on the 3D brain mesh using the ECoG/fMRI visualization and data plotting toolbox.
Output
The final output of the pipeline is:
- a brain_data data structure holding the anatomical mesh data for each hemisphere’s pial and inflated surface.
- an electrode_data data structure holding the coordinates (on the corticla mesh) and metadata of the intracranial electrodes
- Processed anatomical nifti images after normalization, skull-stripping etc.
Environment and software
The pipeline requires a Linux environment (see here about setting up a virtual machine if necessary) with the following software installed:
- MATLAB
- FreeSurfer
- BioImage Suite
- FSL
- AFNI and SUMA
If using BioImage Suite in a publication please reference this properly as: X. Papademetris, M. Jackowski, N. Rajeevan, H. Okuda, R.T. Constable, and L.H Staib. BioImage Suite: An integrated medical image analysis suite, Section of Bioimaging Sciences, Dept. of Diagnostic Radiology, Yale School of Medicine. http://www.bioimagesuite.org.
If using FLIRT in a publication please cite the articles: 1. M. Jenkinson and S.M. Smith. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Medical Image Analysis, 5(2):143-156, 2001. 2. M. Jenkinson, P.R. Bannister, J.M. Brady, and S.M. Smith. Improved optimisation for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17(2):825-841, 2002.
Consult the following installation notes if you’re having trouble:
FreeSurfer
Follow download, installation, registration and configuration instructions on http://freesurfer.net. It takes a few steps but it’s quite straightforward.
One additional step that I needed to make: by default, FreeSurfer is installed to /usr/local. This means you will need root permissions to edit the files there. This is a minor nuisance during installation, for example when you need to create the license.txt file (but getting over this difficulty is part of learning to use Linux, deal with it). However it’s more of a problem when you actually run FS since the Subjects folder, to which all results are written is by default under the same folder (/usr/local/freesurfer/subjects). What I did is to edit the SUBJECTS_DIR variable in /usr/local/freesurfer/SetUpFreeSurfer.sh from the default value to my home folder (in my case, to /home/my_user/freesurfer/subjects). Another minor point - for some reason a lot of the files produced by the freesurfer analysis are marked as hidden files - if you can’t find a file try showing hidden files.
BioImage Suite
Download the BioImageSuite Linux version: http://www.bioimagesuite.org/lands/downloads/index.aspx#page3 (user: anonymous; pwd: bioimagesuite)
Go to the folder where the file has been downloaded to, open a terminal and type:
sudo mkdir /usr/local/BIS
sudo sh
Finally to make it work you need to type:
sudo ln -fs /usr/lib64/libhistory.so.6 /lib64/libhistory.so.5
(or for 32-bit machines and applications: “sudo ln -fs /usr/lib/libhistory.so.6 /lib/libhistory.so.5”. In any case if it doesn’t work, search for a file named libhistory.so.?? and create a link from /lib/libhistory.so.5 to it).
To run BioImageSuite, type:
sh run_bioimagesuite
FSL
Download fslinstaller.py: http://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsldownloads/
Go to the folder where the downloaded file is and enter:
python fslinstaller.py
When prompted for the installation directory, press enter.
Open the file ~/bash_profile (it is hidden) and enter the following at the end:
FSLDIR=/usr/local/fsl
. ${FSLDIR}/etc/fslconf/fsl.sh
PATH=${FSLDIR}/bin:${PATH}
export FSLDIR PATH
To complete the installation log out and log back in.
AFNI
Follow the instructions here.
To fix the error you get when trying to run afni, use a similar fix as the one given before for BioImage Suite:
sudo ln -fs /usr/lib64/libXmu.so.6 /lib64/libXpm.so.4
(I was just guessing this will work and it looks like it does).
Finally, make sure that the AFNI/abin/matlab folder is in your Matlab path definitions.
SUMA
http://afni.nimh.nih.gov/pub/dist/doc/program_help/@SUMA_Make_Spec_FS.html https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/LGI
MRIcron
A simple 3-slice visualization tool for MRI/CT. Does not have a “3D volume” display, but is useful for showing several overlaid images (for example when testing the results of white/gray matter segmentation or brain surface generation). Download: http://www.mccauslandcenter.sc.edu/mricro/mricron/install.html